How to achieve corporate goals: Leadership behavior is often decisive
Reading time: 15 Minuten
Leadership behavior and leadership styles The basic behavior of leaders toward their employees is associated with certain characteristics. A leader can act fairly and empathically or exhibit authoritarian and erratic leadership behavior. Good leaders can inspire, motivate and set an example by being honest, [...]
The basic behavior of leaders toward their employees is associated with certain characteristics. A leader can act fairly and empathically or exhibit authoritarian and erratic leadership behavior. Good leaders can inspire, motivate and set an example by being honest, transparent and open.
Collaborative leadership behavior is by far the most common model and generally leads to the desired success in achieving organizational goals.

Agile leadership behavior as a success factor
Just as every person has different strengths and weakness, this naturally also applies to leaders and their style – an individually formed behavior is also part of one´s personality and character. In addition, an already existing corporate culture and the corporate values can also shape and determine this behavior. An overall agile leadership behavior is in fact the most likely to succeed – and is also basically the focus in the search for ideal leaders.
„A leadership style can have an impact on efficiency, motivation, team cohesion and productivity."
As early as the mid-20th century, the German psychologist Kurt Lewin explored how different leadership styles affect satisfaction and the atmosphere in a group. He was also interested in the effects of leadership styles on efficiency, motivation, team cohesion and productivity. Lewin developed three “classic” leadership behaviors that are, by and large, transferable in the digitally influenced 21st century: the autocratic, the laissez-faire and the collaborative leadership style.
What are the most important leadership behaviors?
Three classic leadership styles according to behavioral psychologist Kurt Lewin:

The autocratic leadership style is based on clear hierarchies and decision-making without much employee involvement. Almost all responsibility lies with supervisors and is not delegated. Instructions are clearly defined and leave little (creative) leeway for employees. This type of leadership style can be effective in crisis situations, for example, since clear instructions are particularly necessary in such times. Nevertheless, it quickly becomes clear that this leadership behavior is meanwhile by far outdated in a digitalized and freedom-oriented working world. It leads to strong dissatisfaction within a team/company, puts limitations on the individual and leads to increased turnover. It tends to be perceived by employees and middle management as a leadership failure.

The complete opposite of this is the laissez-faire leadership style – here the focus is on the independence of the individual employee and the practically unrestricted freedom to make decisions. This is a leadership behavior that might be suitable in creative environments with innovative and independent employees, but one is which the further development of the individual by the leader falls, to a large extent, by the wayside. As a result of the only very sporadic exchange and limited feedback, the leader contributes little to the individual development of the employees and thus to the development of the company.

The collaborative (democratic) leadership style is the style most often mentioned by job applicants in job interviews nowadays, as it is usually the most successful and thus desired by companies. No wonder, it describes the supervisor who probably most employees would like to have: A boss, who involves them in decisions, takes an interest in their needs, provides targeted feedback and assigns responsible tasks. There is regular and transparent communication at eye level and everyone feels that they are pulling together. This is a collaborative form of leadership that undoubtedly has many advantages. There are however, a few possible disadvantages that should not be overlooked. The authority of the leader, i.e. the power to issue directives, can be diluted. It is therefore important for supervisors to position themselves as leaders, to take responsibility and to make decisions, despite the friendly and collaborative interaction.
Bringing together companies and employees collaboratively and without leadership failures
Leaders are the interface between corporate leadership and personnel and carry a great deal of responsibility. On the one hand, they have to realize the company's goals and act in a result-oriented manner. On the other hand, they work with people who need to be motivated, valued and developed. In this interplay between encouraging and challenging, leaders must find their personal and specific leadership style – one that comes across as authentic through their wealth of experience and their own intuition, motivates employees and fits into a globalized and increasingly digital working world.
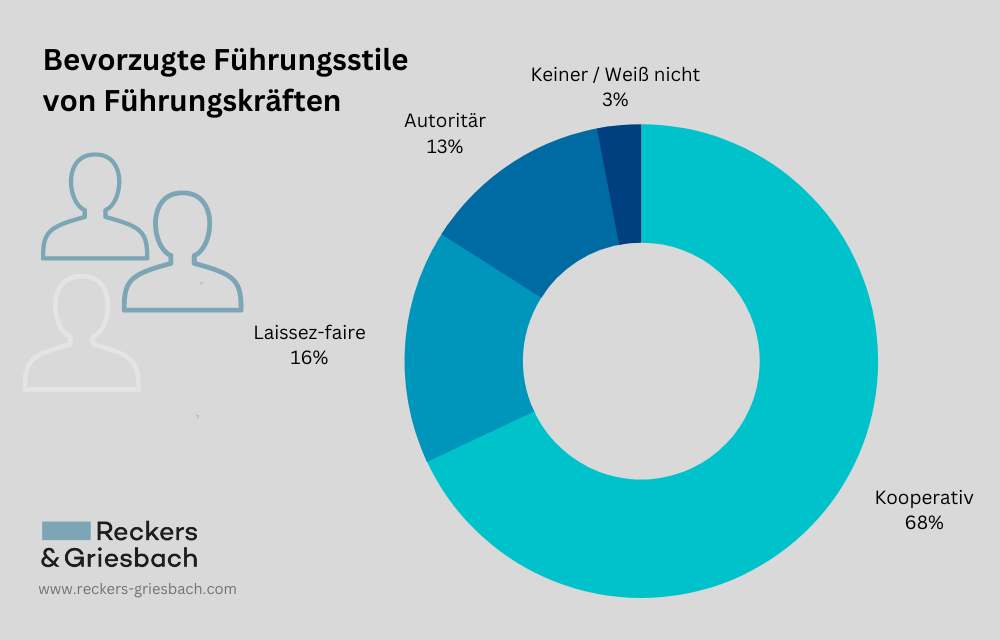
Source: Survey ougov.de, 2018–2019
It is quite evident that collaborative leadership behavior as described above is by far the best way to achieve the desired success in achieving corporate goals.
We fill leadership positions. Permanent and Interim.


